| HOME | HELP | FEEDBACK | SUBSCRIPTIONS | ARCHIVE | SEARCH | TABLE OF CONTENTS |
© American Dairy Science Association, 2005.
Characterization of Days Dry for United States Holsteins
Animal Improvement Programs Laboratory, Agricultural Research Service, USDA, Beltsville, MD 20705-2350
Corresponding author: Melvin Kuhn; e-mail: mkuhn@aipl.arsusda.gov.
This research characterized days dry (DD) for modern US
Holsteins. This included investigation of factors influencing DD,
summarizing variation in herd means as well as within-herd variation,
and estimation of parameters related to DD. Data consisted of
records initiated before 2003 from cows first calving after 1996.
A total of 459,075 records from 295,067 cows in 3527 herds were
included. The overall mean DD was 60.5 d, and standard deviation
among herd means was 5.8 d. Approximately 91% of all herds had
mean DD between 50 and 70 d. There were 41 herds that had mean
DD of 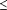 45 d and 2 herds
with mean DD of
45 d and 2 herds
with mean DD of 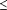 30 d. Some
herds (125) had unusually long mean DD (exceeding 71 d). Variation
across regions of the United States was minimal, although
southwestern herds did show somewhat longer DD than other regions.
Days open (DO) accounted for the most variation in DD with longer DO
leading to longer dry periods. Heritability of DD was 7% and
repeatability 12%. Error correlations indicated that longer dry
periods benefit both milk yield and somatic cell score in the
subsequent lactation. Genetic and permanent environmental
correlations were large, which indicated that 1) bias would result if
genetic evaluations for milk yield included an adjustment for DD, and
2) correction for cow effects is warranted in estimation of DD
effects on performance. The relationship between DD and DO is due
primarily to permanent cow effects. Improved fertility will enhance
the feasibility of shortened dry periods.
30 d. Some
herds (125) had unusually long mean DD (exceeding 71 d). Variation
across regions of the United States was minimal, although
southwestern herds did show somewhat longer DD than other regions.
Days open (DO) accounted for the most variation in DD with longer DO
leading to longer dry periods. Heritability of DD was 7% and
repeatability 12%. Error correlations indicated that longer dry
periods benefit both milk yield and somatic cell score in the
subsequent lactation. Genetic and permanent environmental
correlations were large, which indicated that 1) bias would result if
genetic evaluations for milk yield included an adjustment for DD, and
2) correction for cow effects is warranted in estimation of DD
effects on performance. The relationship between DD and DO is due
primarily to permanent cow effects. Improved fertility will enhance
the feasibility of shortened dry periods.
Key Words: days dry · days open
Abbreviations: DD = days dry · DO = days open · PE = permanent environment.
| HOME | HELP | FEEDBACK | SUBSCRIPTIONS | ARCHIVE | SEARCH | TABLE OF CONTENTS |