| HOME | HELP | FEEDBACK | SUBSCRIPTIONS | ARCHIVE | SEARCH | TABLE OF CONTENTS |
|
| ||||||||
.gif) ,
,
* Animal Improvement Programs Laboratory,
Agricultural Research Service, USDA, Beltsville, MD 20705-2350 Brown Swiss
Association, Beloit, WI 53511-5456
Brown Swiss
Association, Beloit, WI 53511-5456.gif) National Fund for Scientific Research, B-1000 Brussels,
Belgium
National Fund for Scientific Research, B-1000 Brussels,
Belgium Animal Science Unit, Gembloux Agricultural University, B-5030 Gembloux, Belgium
Animal Science Unit, Gembloux Agricultural University, B-5030 Gembloux, Belgium
1 Corresponding author: wiggans{at}aipl.arsusda.gov
Genetic parameters and relative breeding values were
estimated for milking speed of US Brown Swiss dairy cattle.
Owner-recorded milking-speed scores on a scale of 1 (slow) to 8
(fast) were collected by the Brown Swiss Association as part of its
linear type appraisal program starting in 2004. Data were 7,366
records for 6,666 cows in 393 herds. The pedigree file included
information for 21,458 animals born in 1985 or later. Six
unknown-parent groups that each included 4 birth years were defined.
The model included fixed effects for herd appraisal date and
parity-lactation stage and random effects for permanent environment,
animal, and error. Within parity (1, 2, and 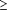 3), 6 groups were defined:
unknown calving date, four 90-d lactation stages, and lactations
with >400 d in milk. Heritability of 0.22 and repeatability
of 0.42 were estimated by average-information REML; residual
variance was 1.13. Little trend in estimated breeding value was
found for cows born from 1999 through 2002. Although solutions
increased with lactation stage for first-parity cows by 0.37,
no clear trend was found for later parities. Genetic evaluations
for milking speed were expressed as relative breeding values
with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 5. The 121 bulls
with
3), 6 groups were defined:
unknown calving date, four 90-d lactation stages, and lactations
with >400 d in milk. Heritability of 0.22 and repeatability
of 0.42 were estimated by average-information REML; residual
variance was 1.13. Little trend in estimated breeding value was
found for cows born from 1999 through 2002. Although solutions
increased with lactation stage for first-parity cows by 0.37,
no clear trend was found for later parities. Genetic evaluations
for milking speed were expressed as relative breeding values
with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 5. The 121 bulls
with 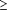 10 daughters had
milking speed evaluations that ranged from 83 to 112 and had
correlations of 0.56 with productive life evaluations and –0.40 with
somatic cell score evaluations. The association of faster milking
speed with lower somatic cell score was not expected. The moderate
heritability found for milking speed indicates that the evaluations
(first released in May 2006) should be useful in detecting bulls with
slow-milking daughters.
10 daughters had
milking speed evaluations that ranged from 83 to 112 and had
correlations of 0.56 with productive life evaluations and –0.40 with
somatic cell score evaluations. The association of faster milking
speed with lower somatic cell score was not expected. The moderate
heritability found for milking speed indicates that the evaluations
(first released in May 2006) should be useful in detecting bulls with
slow-milking daughters.
Key Words: genetic evaluation • milking speed • Brown Swiss
| HOME | HELP | FEEDBACK | SUBSCRIPTIONS | ARCHIVE | SEARCH | TABLE OF CONTENTS |