| HOME | HELP | FEEDBACK | SUBSCRIPTIONS | ARCHIVE | SEARCH | TABLE OF CONTENTS |
|
| ||||||||
Animal Improvement Programs Laboratory, Agricultural Research Service, USDA, Beltsville, MD 20705-2350
1 Corresponding author: duane.norman{at}ars.usda.gov
Genetic and environmental factors that might affect
gestation length (GL) were investigated. Data included information
from >11 million parturitions from 1999 through 2006 for 7 US
dairy breeds. Effects examined were year, herd-year, month, and
age within parity of conception; parturition code (sex and
multiple-birth status); lactation length and standardized milk
yield of cow; service sire; cow sire; and cow. All effects were
fixed except for service sire, cow sire, and cow. Mean GL for
heifers and cows, respectively, were 277.8 and 279.4 d for Holsteins,
278.4 and 280.0 d for Jerseys, 279.3 and 281.1 d for Milking
Shorthorns, 281.6 and 281.7 d for Ayrshires, 284.8 and 285.7 d
for Guernseys, and 287.2 and 287.5 d for Brown Swiss. Estimated
standard deviations of GL were greatly affected by data restrictions
but generally were approximately 5 to 6 d. Year effects on GL
were extremely small, but month effects were moderate. For Holstein
cows, GL was 2.0 d shorter for October conceptions than for
January and February conceptions; 4.7 and 5.6 d shorter for
multiple births of the same sex than for single-birth females
and males, respectively; 0.8 d longer for lactations of 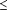 250 d than for lactations of
250 d than for lactations of
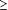 501 d; and 0.6 d shorter for
standardized yield of
501 d; and 0.6 d shorter for
standardized yield of 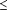 8,000 kg than for yield of
8,000 kg than for yield of 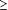 14,001 kg. Estimates for GL heritability from parities 2 to
5 were 33 to 36% for service sire and 7 to 12% for cow sire;
corresponding estimates from parity 1 were 46 to 47% and 10 to 12%.
Estimates of genetic correlations between effects of service sire and
cow sire on GL were 0.70 to 0.85 for Brown Swiss, Holsteins, and
Jerseys, which indicates that those traits likely are controlled by
many of the same genes and can be used to evaluate each other.
More accurate prediction of calving dates can help dairy
producers to meet management requirements of pregnant animals and to
administer better health care during high-risk phases of
animals’ lives. However, intentional selection for either shorter
or longer GL is not recommended without consideration of its
possible effect on other dependent traits (e.g., calving ease and
stillbirth).
14,001 kg. Estimates for GL heritability from parities 2 to
5 were 33 to 36% for service sire and 7 to 12% for cow sire;
corresponding estimates from parity 1 were 46 to 47% and 10 to 12%.
Estimates of genetic correlations between effects of service sire and
cow sire on GL were 0.70 to 0.85 for Brown Swiss, Holsteins, and
Jerseys, which indicates that those traits likely are controlled by
many of the same genes and can be used to evaluate each other.
More accurate prediction of calving dates can help dairy
producers to meet management requirements of pregnant animals and to
administer better health care during high-risk phases of
animals’ lives. However, intentional selection for either shorter
or longer GL is not recommended without consideration of its
possible effect on other dependent traits (e.g., calving ease and
stillbirth).
Key Words: gestation length • breed • twinning • heritability
| HOME | HELP | FEEDBACK | SUBSCRIPTIONS | ARCHIVE | SEARCH | TABLE OF CONTENTS |